I will cover the is How to Migrate Ethereum-Based Tokens to Sidechains in regards to their scalability, performance metrics, and costs of transactions.
If you are a developer or an owner of a project, knowing the ins and outs of how to migrate the tokens will enable you to take advantage of quicker, more efficient networks while still being compatible with Ethereum. Now, let’s dive into the tools, methods, and best practices that are involved.
What Are Sidechains?
Sidechains function as separate blockchains operating simultaneously with a primary blockchain like Ethereum, aiming to enhance the scalability and the throughput of a main blockchain.

They facilitate the movement of assets, for example, tokens, between the main chain and the sidechain via a two-way bridge. This minimizes the burden on the main network while providing quick and cost-effective transactions.
Although sidechains have their own consensus mechanisms, the fact that they are tethered to the main chain makes them a viable option for developers aiming to optimize performance while still using Ethereum.
How to Migrate Ethereum-Based Tokens to Sidechains

Example: Transferring USDC from Ethereum to Polygon with the Polygon Bridge
Step-by-Step Guide
Connect Your Wallet
- Navigate to Polygon bridge, and either connect your MetaMask or Web3 wallet.
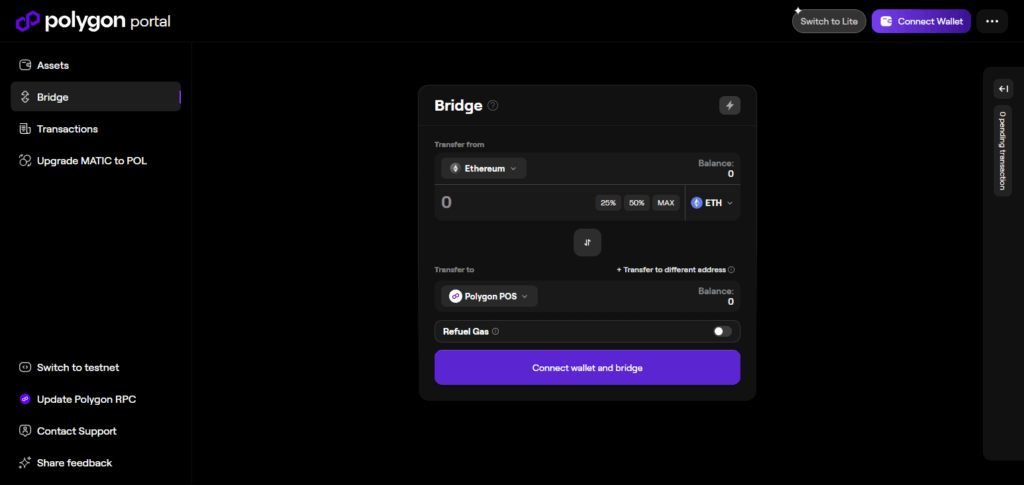
Make sure your wallet is configured to Ethereum Mainnet.
Select the Token to Bridge
- From the token list, select USDC.
- Specify the quantity in the box (ex: 100 USDC).
Initiate the Transfer
- Select “Transfer” and check the estimated gas fee as well as the bridging duration.
- Validate the payment in MetaMask.
Wait for Confirmation
- Your USDC will be locked on Ethereum, and then equivalent USDC will be minted on Polygon.
- This is done in around 7–15 minutes.
Switch to Polygon Network
- Change your wallet to Polygon network after confirmation.
- You will now have 100 bridged USDC available in your wallet to spend on Polygon dApps.
Other Place Where to Migrate Ethereum-Based Tokens to Sidechains
Gnosis Chain
Gnosis Chain greatly focuses on governance and low fees which makes it a good candidate for moving Ethereum-based tokens to a sidechain. It is designed for smooth Ethereum integration, so bridges can be utilized for token transfers with minimal coding changes.
Its most distinctive feature is a community governance model together with a validation system based on open, secure, and trustable processes. Gnosis Chain is immensely beneficial to projects aiming for community-driven eco-friendly infrastructure because it provides a reliable ecosystem for scalable token operations.
Why Migrate Tokens to a Sidechain?
Pay Less For Transactions: Compared to Ethereum’s mainnet, sidechains have significantly lower gas fees which make microtransactions as well as frequent transfers cost effective.
Quick Transactions: Sidechains are less congested compared to the main network enhancing the user experience in DeFi, gaming, and other dApps with faster confirmation times.
Increased Scalability: The ability to offload transactions onto sidechains helps Ethereum reduce the strain on its network, allowing it to grow without impacting performance.
Better Overall Experience: Faster transaction speeds and lower fees provide users with a better overall experiencing trading.
Operability Between Different Blockchains: Used sidechains are known to have bridge and protocol support for moving tokens and info between other blockchains, therefore increasing usability.
Further Tailored Blockchains: Adjusting the sidechain parameters such as the consensus mechanism or block time allows developers to tailor the environment to its applications.
Reduction Of Carbon Footprint: The negative impacts on the environment caused by transactions are reduced because most sidechains have proof-of-stake and eco-friendly consensus mechanisms.
Security Considerations
Bridge Exploit Risks: Cross-chain bridges are often targets for exploits, with potential devastating consequences. The tokens may be permanently lost or stolen unless a full audit of the bridge’s smart contracts has been conducted.
Trustless Mechanism Security: Sidechains that utilize a different type of consensus mechanism such as less decentralized ones than Ethereum, lose trust in the sidechain and become prone to manipulation.
Logic Errors in Smart Contracts: Smart contracts that are to be migrated may not function as intended in the new setting. A comprehensive test is critical to avoid unforeseen logic errors.
Censorship Resistance Risks: Some sidechains are dependent on a small group of validators or a central controlling body which poses greater threats regarding censorship resistance.
Lesser Security Sufficiency: As compared to Roll ups, most sidechains do not inherit the Ethereum full security model, making them more susceptible to attacks.
Token Mapping Between Chains Risks: Improper management of mapping the tokens between the chains results in inconsistencies, loss or worst case, duplication of tokens.
Anomaly Monitoring: Analyzing for abnormal activity, especially during and after migration, requires constant monitoring. Create redundancy for alerting systems and error response plans for breaches or faults.
Best Practices and Tips

Select Known Sidechains with Audited Bridges: Select known sidechains with audited bridges such as Polygon and Gnosis Chain for their reliability and security.
Complete All Testing on Testnets: Defect scanning, validation, and correction of all bugs and conflicts in your token and contracts should be done on the sidechain’s testnet to ensure your copy is polished before going live.
Keep Up with Secured Smart Contracts: Make sure that your tokens stay within the borders of accepted standards which include ERC-20 or ERC-721, granting cross-chain cooperation without any issues.
Perform Smart Contract and Bridges Audits: Smart contracts alongside bridges should be evaluated for security gaps that bridges and contracts should never have, especially before a mainnet launch.
Interact with Users and Keep Them Up to Date: Explain the migration process to the users using simplified instructions for changing wallets, dApps and the sidechain itself.
Set Up Activity Monitoring Systems: Post-migration, track token activities to ensure proper operation and discover any deviations.
Employ Timelocks or Multisig for Admin Limits: Defend sidechain centralization by ensuring no single failsafe is present within the administrative functions to bolster security.
Account for Potential Enhancements in the Future: Don’t lock yourself out from changing governance, upgrades, or migrating back to Ethereum by setting rigid terms.
Conclusion
In conclusion the advantages of migrating Ethereum-based tokens to sidechains helps to bypass Ethereum’s constrictions on cost, speed, and scalability.
With proper sidechain selection, secure bridge usage, and reliable deployment procedures, developers can improve performance and user experience with no tradeoff on Ethereum compatibility.
Although this approach demands comprehensive planning and strong coordination among stakeholders, the cost-effective ecosystem that emerges after the scaling dApps in Web3 is a strong motivator.
FAQ
What is needed to migrate tokens to a sidechain?
You need a compatible wallet, the token’s smart contract, access to a trusted bridge, and possibly minor code modifications depending on the sidechain.
Can any Ethereum token be migrated to a sidechain?
Most standard tokens like ERC-20 or ERC-721 can be migrated, but compatibility depends on the sidechain’s support for these standards.
Are token migrations reversible?
Yes, in most cases, tokens can be bridged back to Ethereum if the sidechain supports two-way bridging. Always verify this before migrating.








